How To Bill Endoscopic Transoral Incisionless Fundoplasty With Laparoscopic Hiatal Hernia Repair
February. 16, 2022
Gastroesophageal reflux illness (GERD) is a common reason for American adults to see a gastroenterologist and the leading indication for upper endoscopy. In addition to its affect on quality of life, chronic GERD is a risk factor for numerous adverse events, such equally esophageal stricture formation, Barrett's metaplasia and esophageal adenocarcinoma, thus necessitating acceptable diagnosis and treatment of this mutual entity.
Until recently, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) were deemed the treatment of selection for the majority of individuals with early on illness and balmy to moderate chronic symptoms, with plenty of study results demonstrating their efficacy. Withal, researchers estimate that most a quarter of individuals experience a partial or suboptimal response to PPIs for a variety of reasons, including noncompliance and failure of the drugs to address an underlying incompetent gastroesophageal valve function, which is an anatomical aberration not corrected by this class of medications. Additionally, although the accented risk is low, multiple studies have shown an association between long-term PPI use and potential adverse wellness outcomes.
Surgical interventions, including Nissen fundoplication and the more commonly performed laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication, are available for those individuals who crave anatomic correction. This can include individuals who are intolerant to PPIs, those who are concerned about long-term medication use, or those who have advanced anatomical abnormalities of the gastroesophageal junction (such every bit a large hiatal hernia) preventing appropriate valve functioning. Both of these procedures, however, are associated with complications inherent in surgical intervention and can have chronic side effects such as bloating and dysphagia. And some patients will have backsliding of symptoms requiring re-initiation of medical therapy.
These concerns have fueled interest in the search for a noninvasive endoscopic therapeutic culling that's both prophylactic and effective in bridging the current gap in GERD management for appropriately selected patients. Endoscopic methods to control reflux in the Us include the Stretta procedure, Medigus Ultrasonic Surgical Endostapler (MUSE) and transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF).
The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guidelines published in 2022 note that endoscopic anti-reflux therapy may exist considered for select patients with GERD. In this Q&A, Barham Chiliad. Abu Dayyeh, Chiliad.D., 1000.P.H., a gastroenterologist specializing in advanced endoscopic procedures at Mayo Clinic's campus in Rochester, Minnesota, answers primal questions almost TIF and provides an overview of recent research findings evaluating the efficacy of this approach.
What is the goal of TIF and how is it performed?
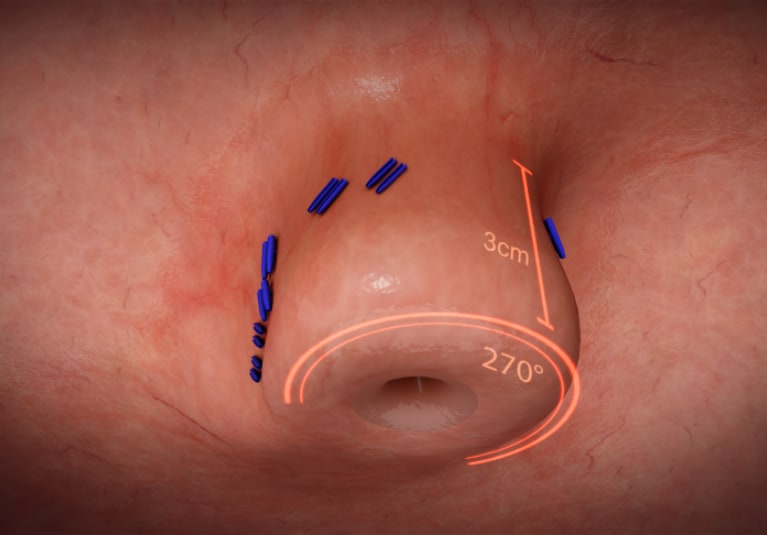
The goal of TIF is to restore the integrity of the gastroesophageal valve by creating a 270-degree esophagogastric wrap around the distal esophagus, anchored by multiple polypropylene fasteners, which have similar strength to iii.0 sutures. The process is performed through the mouth with no surgical incisions using the EsophyX Z+ device.
Which patients tin can benefit from TIF?
Individuals who can do good from the TIF process include:
- Patients with typical GERD symptoms and suboptimal command of their symptoms on PPIs who practice non have a large hiatal hernia or esophageal motion bug
- Patients with GERD symptoms and mild to moderate anatomic abnormalities of the gastroesophageal junction valve part that require correction
- Patients preferring an alternative direction strategy for their GERD that does non involve long-term medication employ
At Mayo Clinic, nosotros take been offering the TIF procedure for a few months. Multiple patients take undergone the procedure with no complications and achieved excellent control of their GERD symptoms in the curt term.
What do recent research results show about the safety and efficacy of TIF?
Results from the Randomized EsophyX vs. Sham, Placebo-Controlled Transoral Fundoplication (RESPECT) trial published in Gastroenterology in 2022 demonstrated that TIF was an effective treatment for patients with GERD symptoms, specially in those with persistent regurgitation despite PPI therapy, based on an evaluation half dozen months subsequently the procedure. The trial randomized 87 patients to TIF with a placebo versus 42 patients to a sham procedure and a PPI. A total of 67 percent of patients in the TIF arm no longer had regurgitation compared with 45 percent in the sham arm.
A study published in The American Journal of Gastroenterology in 2022 followed patients for 12 months, as they were randomized to TIF versus PPI. The primary result of the written report was GERD-related quality of life, which improved significantly with TIF compared with baseline and PPI use only. The authors concluded that although TIF improved GERD-related quality of life and yielded brusk-term improvements in the anti-reflux barrier in some individuals, no long-term objective reflux control was achieved.
A double-blind, sham-controlled report of patients with GERD who were chronic PPI users randomized 88 patients as, and lx percent of patients remained costless of symptoms at six months after intervention. Based on these results, published in Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics in 2022, the authors concluded that TIF is effective in people with chronic PPI-dependent GERD when followed for half dozen months.
Karim S. Trad, M.D., and co-authors shared results from two trials worth noting. In an commodity published in BMC Gastroenterology in 2022, they shared the results of a randomized crossover study involving 40 patients receiving TIF and 23 receiving high-dose PPIs who were followed for six months earlier crossing over. Six months after TIF, the majority of crossover patients (71 percentage) were off PPIs. At the end of the study (at 12 months), only xviii percentage of the index TIF grouping patients were using PPIs.
In 2022, the five-year TEMPO trial results were published in Surgical Innovation by the same authors, offering the longest elapsing of follow-up to TIF shared thus far. In this randomized controlled crossover study, 44 participants completed the study at five years. Regurgitation resolved in 86 per centum of study participants, and atypical symptoms improved in 80 percent of report participants. The authors noted that no serious agin events were reported during the duration of the study. Just three participants underwent a repeat procedure by the end of the five years. Furthermore, at v years, 66 pct of participants had discontinued their daily PPI intake.
Given these findings, what long-term part do you foresee for TIF in the handling of GERD?
The bike of innovation in endoscopy has yielded several revolutionary changes in the minimally invasive management of unlike GI disorders, and GERD is i of these targets. The TIF procedure offers accordingly selected patients with bothersome symptoms the opportunity to improve their quality of life without resorting to long-term medication employ or major surgical interventions. When adequately implemented in the confines of comprehensive multidisciplinary programs, interventions such as TIF will span the current GERD management gap and offer an constructive solution to many patients suffering with this chronic disorder.
For more information
Hunter JG, et al. Efficacy of transoral fundoplication vs omeprazole for handling of regurgitation in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2022;148:324.
Witteman BPL, et al. Randomized controlled trial of transoral incisionless fundoplication vs. proton pump inhibitors for handling of gastroesophageal reflux disease. American Periodical of Gastroenterology. 2022;110:531.
Håkansson B, et al. Randomised clinical trial: Transoral incisionless fundoplication vs. sham intervention to control chronic GERD. Comestible Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2022;42:1261.
Trad KS, et al. Efficacy of transoral fundoplication for treatment of chronic gastroesophageal reflux illness incompletely controlled with high-dose proton-pump inhibitors therapy: A randomized, multicenter, open label, crossover written report. Gastroenterology. 2022;14:174.
Trad KS, et al. The TEMPO trial at 5 years: Transoral fundoplication (TIF ii.0) is rubber, durable, and cost-effective. Surgical Innovation. 2022;25:149.
Source: https://www.mayoclinic.org/medical-professionals/digestive-diseases/news/transoral-endoscopic-incisionless-fundoplication/mqc-20454990
Posted by: krierequadvance.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Bill Endoscopic Transoral Incisionless Fundoplasty With Laparoscopic Hiatal Hernia Repair"
Post a Comment